ASP.NET 4 Caching
by.shaaz
Caching Overview
A cache is made up of a pool of entries. Each entry has data along with a tag, which specifies the identity of the data in the backing store of which the entry is a copy.In real life, Cache is very simple. If you take the life cycle of an ant, it reserves the food during the summer days for the usage of winter. In a similar line, IT system reserves the frequent usage content for the future request/kit to avoid the redundant operation.
When the cache client (a CPU, web browser, operating system) needs to access the data presumed to exist in the backing store, it first checks the cache. If an entry can be found with a tag matching that of the desired data, the data in the entry is used instead. This situation is known as a cache hit.
CPUs and hard drives frequently use a cache, as do web browsers and web servers. Let's see the caching mechanism at Core level.
Caching at Core Level
A CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations. As long as most memory accesses are cached memory locations, the average latency of memory accesses will be closer to the cache latency than to the latency of main memory. Core/Primary cache is the fastest form of storage. Because it's built in to the chip with a zero wait-state (delay) interface to the processor's execution unit, it is limited in size. With this concept, 3 levels of Core Caching is represented from the OS point of view.
There are few popular Caching algorithms based on key parameters (like hit rate, recent usage, frequent usage). The most popular ones are Belady optimal algorithm, Least recent used (LRU), Random Replacement, Most recently used (MRU), Multi Queue Caching, Segmented LRU, etc.
ASP.NET Caching
With these fundamentals, ASP.NET Framework enables programmers to take advantage of caching without requiring to write a lot of code to deal with the complexities of caching, such as cache expiration, updates, and memory management. There are two different types of caching in ASP.NET:- Application caching
- Page output caching
Application Caching
Application caching is nothing but a collection of in memory objects. It's automatically deallocated based on memory limitation, time limit and few other vital dependencies. It's also termed as application data caching because the scope of these in memory objects are at the application level. In ASP.NET web based context, this cache object exists for the entire web application, can be shared across the user sessions and web requests.In simple terms, Application caching can be called as Global Data Container (GDC). As the name stands, Global Data Container is in the memory storage box to hold the shared data across the application.
A similar concept is extended to the latest computing, i.e., Cloud Computing. Microsoft Azure platform executes the application caching to improve the system performance. The concept is drafted in the below diagram:
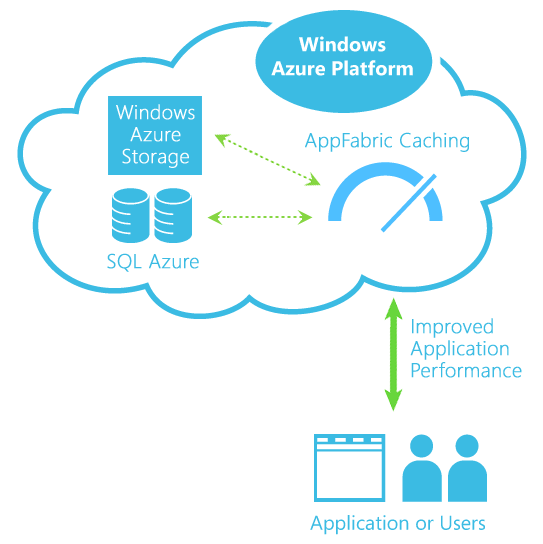
Storing into Application Cache
ASP.NET provides built in Cache object fromSystem.Web.Caching namespace. This object contains 'Insert' method to store any collection into the application cache. Let's see the key parameters for
Insert method of Cache object. - Key: This is the primary name to access the cached object in the
Cachecollection. The key must be unique in the cache. - Value: This is the data as an
Objectthat you want to cache. - Dependencies: It is the associated item for
Cache. Framework will trigger the signal during the changes in this dependency object. - AbsoluteExpiration: This is the time as a
DateTimeobject at which the object should be removed from the cache. - SlidingExpiration: This is the time as a
TimeSpanobject after which the object should be removed from the cache if it has not been accessed by a user. - Priority: This is a
CacheItemPriorityenumeration value that you can use to determine which objects are removed first during scavenging (i.e., when memory starts to run low). Lower priority objects are removed sooner. - onRemoveCallback: This is an event handler that is called when the object is removed from the cache. This can be
nullif you don’t want to specify a callback method.
Code Snippet
using System.Web.Caching;
public partial class _Default : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected override void OnPreInit(EventArgs e)
{
Cache["CompName"] = "ABCD Corporation";
Cache["CompSymbol"] = "ABC";
Cache["CEO"] = "First Last";
// Programmatically Insert operation
Cache.Insert("LastTrade", ReadFeed(LastTradePrice),
null, DateTime.Now.AddHours(8), Cache.NoSlidingExpiration);
//Cache Dependency operation
System.Web.Caching.CacheDependency FeedDepend =
new System.Web.Caching.CacheDependency(Server.MapPath("Feed.xml"));
Cache.Insert("MarketPrice", ReadFeed(CurrentPrice),
FeedDepend, Cache.NoAbsoluteExpiration, Cache.NoSlidingExpiration);
}
}
Code Summary
System.Web.Caching is the namespace supplied by ASP.NET Framework to manipulate the caching operations. It has been included in the first line. Cache content is getting loaded in PreInit state of the page. Cache storage functionality starts from the fourth line of the source code. Based on the working knowledge with
Session or similar objects, Cache object
would be similar. Programmers can assign items directly to the cache by
giving them a name (key) and assigning them an object (value). In the fourth line of the above code, Company Name is stored in the cache with the key '
CompName'. Cache object is the global container object suppliant by Framework at application level. In the similar way, 'CompSymbol' and 'CEO' info are stored in global Cache object. By using the
Insert method, add an item to the cache and
control how that item gets removed from the cache. This functionality
includes automatic removal based on a specific period of time. Insert has a number of overloads based on the many parameters you can set when adding an item to the cache. LastTrade key insert method reserves the content from LastTradePrice, for the next 8 hours. Later, LastTrade cache automatically expires. In ASP.NET Framework, a cache dependency links a cached item to something else such as a file or another item in the cache. ASP.NET monitors the dependency and invalidates the cache if the dependent item changes. In the above code sample, cache dependency is based on Feed.xml file. When this dependent feed file of the cache get updated, the object is removed from the cache. Apparently, we can use '
OnRemoveCallback' delegate to execute the operation on removal event.
No comments:
Post a Comment